Lactate threshold vs vo2 max – In the realm of athletic performance, lactate threshold and VO2 max stand as crucial metrics that define an athlete’s capabilities. Understanding their relationship is key to unlocking optimal training strategies and maximizing results.
Lactate threshold, the point at which the body can no longer efficiently clear lactic acid, and VO2 max, the maximum volume of oxygen the body can utilize, provide valuable insights into an athlete’s endurance and aerobic capacity.
Lactate Threshold (LT)
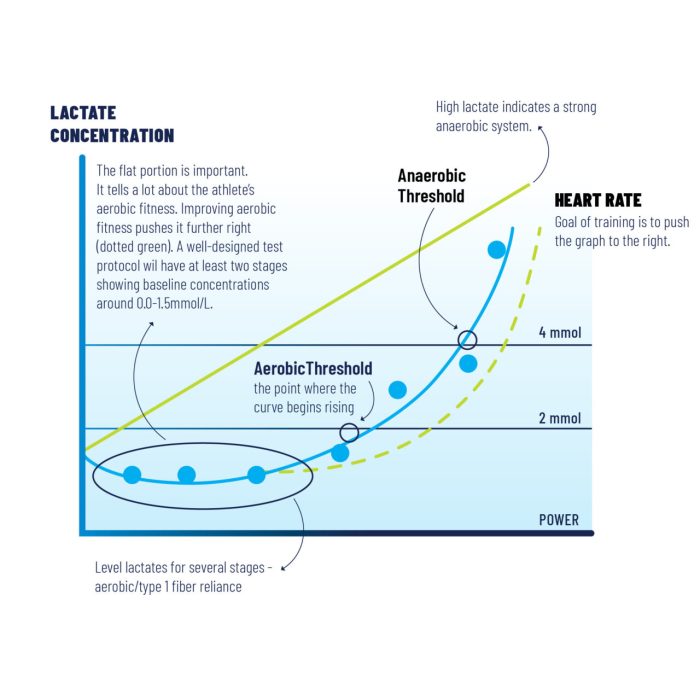
Lactate threshold (LT) is the point during exercise at which the body begins to produce lactate faster than it can be removed. Lactate is a byproduct of anaerobic metabolism, which is the process of producing energy without oxygen. As exercise intensity increases, the body relies more on anaerobic metabolism and produces more lactate.
LT is the point at which the body can no longer clear lactate from the bloodstream as quickly as it is being produced.
Measurement of LT
LT can be measured using a variety of methods, including:
- Blood lactate testing:This involves taking a blood sample and measuring the lactate concentration. LT is typically defined as the lactate concentration at which there is a sharp increase in blood lactate levels.
- Respiratory exchange ratio (RER):This is the ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen consumed. As exercise intensity increases, RER increases. LT is typically defined as the point at which RER begins to increase rapidly.
- Heart rate:Heart rate typically increases linearly with exercise intensity. However, at LT, heart rate often increases more rapidly.
LT Values
LT values vary widely between individuals. Some factors that can affect LT include:
- Fitness level:Fitter individuals typically have a higher LT than less fit individuals.
- Training status:Endurance training can increase LT.
- Genetics:Some individuals are genetically predisposed to have a higher LT than others.
Typical LT values for untrained individuals range from 50% to 60% of VO2 max. For trained endurance athletes, LT values can be as high as 80% of VO2 max.
VO2 Max
VO2 max, or maximal oxygen consumption, is the maximum amount of oxygen that the body can utilize during intense physical exercise. It is a key indicator of cardiovascular fitness and endurance performance.
Lactate threshold and VO2 max are important metrics for endurance athletes. Just like the ancient Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas mapped out their vast territories ( mayans aztecs and incas map ), understanding these thresholds can help athletes navigate their fitness journey.
By pushing beyond their lactate threshold, they can improve their endurance and performance, just as the ancient civilizations expanded their empires by exploring new territories.
Measuring VO2 max provides valuable insights into an individual’s ability to sustain prolonged physical exertion. Higher VO2 max values are associated with improved endurance, faster recovery times, and overall better health outcomes.
Methods to Measure VO2 Max
There are several methods used to measure VO2 max, including:
- Treadmill Test:Involves running on a treadmill with increasing intensity until exhaustion.
- Cycle Ergometer Test:Similar to the treadmill test, but performed on a stationary bike.
- Indirect Calorimetry:Measures oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production using a specialized mask or mouthpiece.
VO2 Max Values
VO2 max values vary significantly among individuals based on factors such as age, gender, training level, and genetics.
Average VO2 Max Values for Different Age Groups:
| Age Group | Men (mL/kg/min) | Women (mL/kg/min) |
|---|---|---|
| 20-29 | 42-46 | 36-40 |
| 30-39 | 38-42 | 32-36 |
| 40-49 | 34-38 | 28-32 |
| 50-59 | 30-34 | 24-28 |
| 60-69 | 26-30 | 20-24 |
VO2 Max Values for Elite Athletes:
Elite endurance athletes, such as marathon runners and cyclists, typically have VO2 max values ranging from 60 to 80 mL/kg/min or higher.
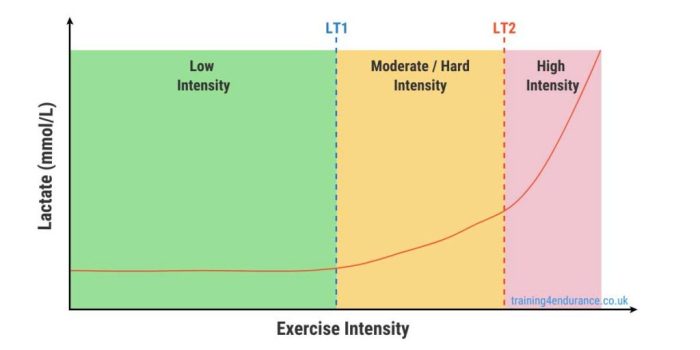
Relationship between LT and VO2 Max
Lactate threshold (LT) and VO2 max are closely related physiological markers that provide valuable insights into an individual’s fitness level. LT represents the point at which the body starts to accumulate lactate in the blood, while VO2 max represents the maximum volume of oxygen the body can use during exercise.
LT as an Estimator of VO2 Max
LT can be used as an indirect estimate of VO2 max. A well-established formula, known as the LT-VO2 max relationship, states that VO2 max is approximately equal to LT multiplied by a factor of 1.15 to 1.25. This relationship suggests that individuals with a higher LT will generally have a higher VO2 max.
Individual Variations
The relationship between LT and VO2 max can vary among individuals. Factors such as training status, muscle fiber composition, and genetics can influence the correlation. For instance, well-trained endurance athletes may have a higher LT compared to untrained individuals, which in turn corresponds to a higher VO2 max.
Example
Consider two individuals, A and B. Individual A has an LT of 4 mmol/L, while Individual B has an LT of 6 mmol/L. Using the LT-VO2 max relationship, we can estimate that Individual A’s VO2 max is approximately 4.6-5.0 mmol/L (4 mmol/L x 1.15-1.25),
and Individual B’s VO2 max is approximately 7.2-7.8 mmol/L (6 mmol/L x 1.15-1.25).
Training Implications
Understanding your LT and VO2 max can significantly enhance your training program by optimizing intensity and duration. Training within specific zones based on these metrics can effectively improve performance and fitness levels.
Training Zones
Training zones are ranges of intensity expressed as a percentage of LT or VO2 max. Each zone elicits specific physiological adaptations:
- LT Zone (75-90% of LT):Improves lactate tolerance and endurance capacity.
- VO2 Max Zone (90-100% of VO2 max):Enhances maximal oxygen uptake and cardiovascular efficiency.
- Moderate Intensity Zone (60-75% of LT):Builds aerobic base and improves endurance.
- Easy Intensity Zone (Below 60% of LT):Promotes recovery and facilitates adaptations.
Training Protocols
Incorporating LT and VO2 max data into training protocols involves varying intensity and duration based on specific goals:
- LT Interval Training:Repeated intervals at LT intensity to enhance lactate tolerance.
- VO2 Max Intervals:Short, intense intervals at VO2 max intensity to improve maximal oxygen uptake.
- Progressive Overload:Gradually increasing training intensity and duration over time to continually challenge the body.
- Polarized Training:Alternating between high-intensity and low-intensity training to optimize adaptations for both LT and VO2 max.
Factors Affecting LT and VO2 Max: Lactate Threshold Vs Vo2 Max
LT and VO2 max are influenced by various factors, including genetics, training, and nutrition.
Genetics
Genetic factors play a significant role in determining LT and VO2 max. Individuals with certain genetic predispositions may have naturally higher or lower levels of these physiological parameters. For instance, studies have shown that genetic variants in genes related to muscle fiber composition and oxidative capacity can influence LT and VO2 max.
Training
Training is a crucial factor that can enhance both LT and VO2 max. Regular exercise, particularly endurance training, stimulates adaptations in the body that improve the ability to utilize oxygen and produce energy efficiently. Over time, training can increase the number of mitochondria in muscle cells, enhance blood flow, and improve the body’s capacity to clear lactate.
Nutrition
Nutrition plays a supportive role in optimizing LT and VO2 max. A balanced diet that provides adequate carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential for fueling exercise and supporting recovery. Specific nutrients, such as carbohydrates, can help maintain glycogen stores and delay the onset of fatigue during high-intensity exercise.
Examples, Lactate threshold vs vo2 max
The impact of these factors can vary significantly between individuals. For instance, an individual with favorable genetics may have a naturally high VO2 max, while someone with less favorable genetics may have to work harder through training to achieve similar levels.
Similarly, a well-trained athlete with a balanced nutrition plan may have a higher LT than an untrained individual with a poor diet. Understanding these factors can help individuals tailor their training and nutrition strategies to optimize their LT and VO2 max.
LT and VO2 Max in Different Populations
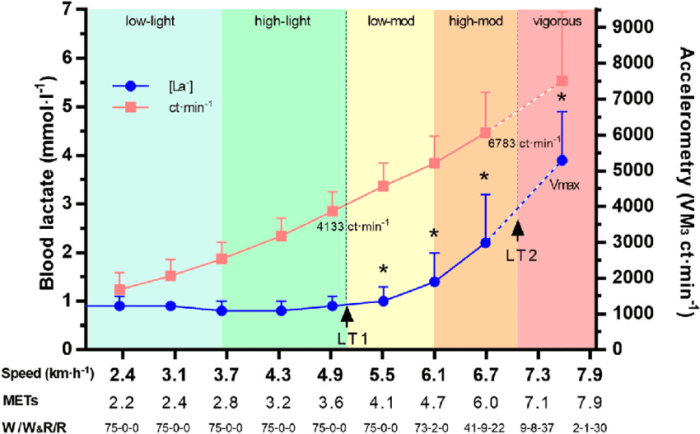
Individuals from different populations exhibit variations in their LT and VO2 max values, reflecting differences in their physical fitness, training status, and overall health. Understanding these variations is crucial for tailoring training programs and optimizing performance.
Athletes vs. Sedentary Individuals
Athletes typically possess higher LT and VO2 max values compared to sedentary individuals. Regular training and conditioning enhance their cardiovascular fitness, allowing them to sustain higher lactate levels and utilize oxygen more efficiently during exercise.
Individuals with Health Conditions
Individuals with certain health conditions may have altered LT and VO2 max values. For instance, individuals with heart disease or chronic respiratory conditions often have reduced VO2 max due to limitations in cardiac or pulmonary function.
Implications for Training and Performance
The differences in LT and VO2 max across populations have implications for training and performance. Athletes can push their training intensity closer to their LT, enabling them to improve lactate tolerance and endurance capacity. In contrast, sedentary individuals may need to start with lower intensities and gradually increase them as their fitness improves.
Advanced Concepts

Moving beyond the basics, this section delves into advanced concepts surrounding lactate threshold (LT) and VO2 max, exploring their intricate relationship with critical power and their significance in sports science and performance analysis.
Critical Power and Its Relationship with LT and VO2 Max
Critical power (CP) represents the highest sustainable power output that an individual can maintain over an extended period, typically for more than 30 minutes. It’s closely related to both LT and VO2 max.
CP is closely associated with the onset of blood lactate accumulation, similar to LT. As exercise intensity increases beyond CP, lactate production exceeds clearance, leading to a rise in blood lactate levels. This relationship between CP and LT suggests that CP may be a more accurate predictor of endurance performance than LT in certain circumstances.
Furthermore, CP is linked to VO2 max. Studies have shown that CP is typically around 75-90% of VO2 max. This relationship implies that improving VO2 max can also enhance CP, and vice versa.
Use of LT and VO2 Max Data in Sports Science and Performance Analysis
LT and VO2 max data are invaluable tools in sports science and performance analysis, providing insights into an athlete’s physiological capabilities and potential for improvement.
These metrics are used to:
- Assess an athlete’s current fitness level and track progress over time.
- Identify areas for improvement in training programs.
- Predict performance in specific events.
li>Develop individualized training plans tailored to an athlete’s strengths and weaknesses.
Examples of LT and VO2 Max Data in Advanced Training and Research
LT and VO2 max data are not just theoretical concepts but have practical applications in advanced training and research:
- Interval training:LT and VO2 max data can guide the intensity and duration of interval training sessions to maximize adaptations and improve performance.
- Altitude training:Research has shown that altitude training can increase both LT and VO2 max, potentially enhancing endurance performance.
- Nutritional strategies:LT and VO2 max data can inform nutritional strategies to optimize energy availability during training and competition.
Helpful Answers
What is the significance of lactate threshold in running?
Lactate threshold indicates the pace at which lactic acid accumulation outpaces the body’s ability to remove it, leading to fatigue and a decline in performance.
How can VO2 max be improved?
VO2 max can be enhanced through regular endurance training, such as running, cycling, or swimming, which gradually increase the body’s capacity to utilize oxygen.
What is the relationship between lactate threshold and VO2 max?
Lactate threshold typically occurs at around 70-85% of VO2 max, and it serves as a predictor of an athlete’s endurance capabilities.