Mcgraw hill connect accounting answers chapter 4 – Embark on a journey through the intricacies of accounting with McGraw-Hill Connect Accounting Answers Chapter 4. This comprehensive guide unravels the fundamental principles, empowering you to navigate the accounting cycle with confidence and precision.
Delve into the intricacies of journal entries, posting, and adjusting entries, gaining a thorough understanding of how transactions are meticulously recorded and processed. Explore the significance of financial statements, deciphering their purpose and components to effectively communicate financial performance.
Key Concepts
The fundamental accounting principles covered in Chapter 4 of McGraw-Hill Connect Accounting are:
- Accrual accounting: Transactions are recorded when they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
- Going concern: The business is assumed to continue operating in the foreseeable future.
- Matching principle: Expenses are matched to the revenues they generate.
The accounting cycle consists of the following stages:
- Recording transactions in a journal.
- Posting journal entries to the general ledger.
- Preparing a trial balance.
- Making adjusting entries.
- Preparing financial statements.
- Closing temporary accounts.
It is important to record transactions accurately and consistently to ensure the reliability of financial statements.
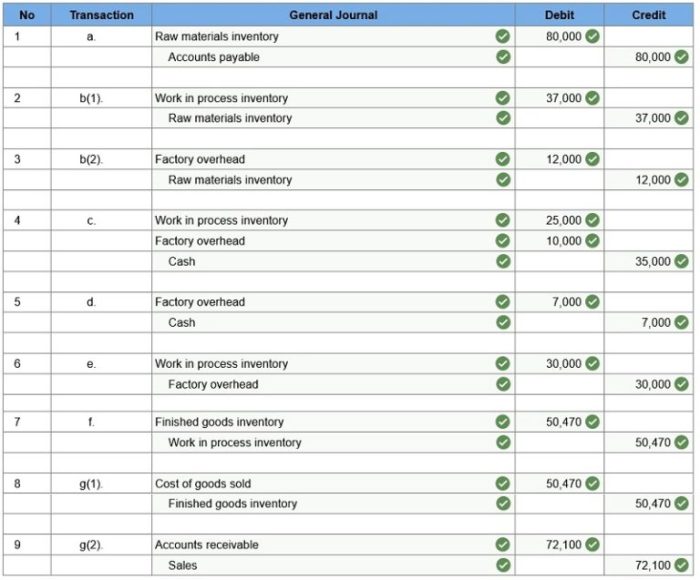
Journal Entries and Posting: Mcgraw Hill Connect Accounting Answers Chapter 4
To analyze business transactions and create appropriate journal entries, follow these steps:
- Identify the accounts affected by the transaction.
- Determine the debit and credit amounts for each account.
- Record the journal entry in the general journal.
To post journal entries to the general ledger, follow these steps:
- Transfer the debit amount to the debit side of the appropriate account.
- Transfer the credit amount to the credit side of the appropriate account.
T-accounts can be used to track account balances.
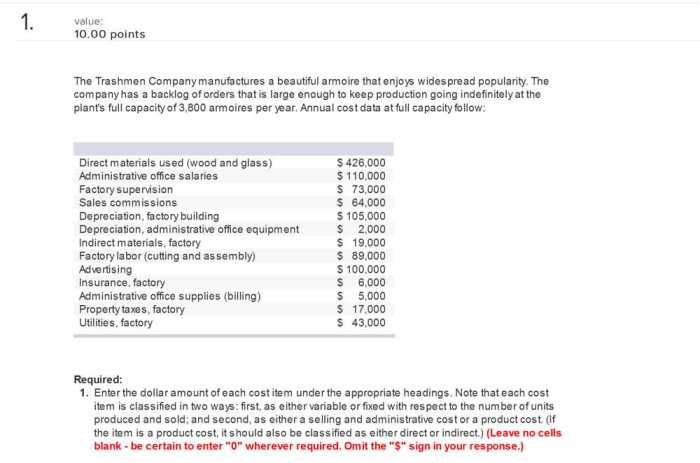
Adjusting Entries
Adjusting entries are made at the end of an accounting period to update account balances and ensure that financial statements are accurate.
Common types of adjusting entries include:
- Accruals: To record revenue earned but not yet billed or expenses incurred but not yet paid.
- Deferrals: To record revenue received in advance or expenses paid in advance.
Adjusting entries impact financial statements by:
- Updating account balances.
- Matching expenses to revenues.
- Ensuring that financial statements reflect the true financial position of the business.
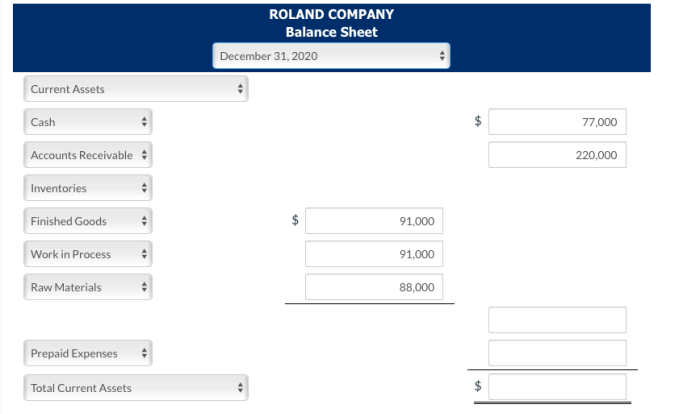
Financial Statements
The three main financial statements are:
- Balance sheet: Shows the financial position of a business at a specific point in time.
- Income statement: Shows the financial performance of a business over a period of time.
- Statement of cash flows: Shows the inflows and outflows of cash over a period of time.
To prepare financial statements using the adjusted trial balance, follow these steps:
- Transfer the account balances from the adjusted trial balance to the appropriate financial statement.
- Calculate the net income or loss.
- Complete the financial statement.
Closing Entries
Closing entries are made at the end of an accounting period to close temporary accounts and transfer their balances to the retained earnings account.
To prepare closing entries, follow these steps:
- Close revenue accounts to the income summary account.
- Close expense accounts to the income summary account.
- Close the income summary account to the retained earnings account.
Closing entries impact financial statements by:
- Zeroing out temporary accounts.
- Transferring net income or loss to the retained earnings account.
- Preparing the business for the next accounting period.
Q&A
What are the key concepts covered in Chapter 4 of McGraw-Hill Connect Accounting?
Chapter 4 delves into the fundamental principles of accounting, the accounting cycle, and the importance of accurate and consistent transaction recording.
How do I create journal entries and post them to the general ledger?
The guide provides step-by-step instructions on analyzing transactions, creating journal entries, and posting them to the general ledger using T-accounts to track account balances.
What is the purpose of adjusting entries and how do they impact financial statements?
Adjusting entries ensure that financial statements accurately reflect the financial position of a company at a specific point in time. They correct for unrecorded transactions and events that have occurred but have not yet been recorded.