Introducing the Motion Graph Practice Questions Answer Key, an invaluable resource designed to empower students with the knowledge and skills to excel in interpreting motion graphs. Through a series of meticulously crafted questions and detailed answer explanations, this key unlocks the secrets of motion analysis, enabling students to confidently tackle complex problems and gain a deeper understanding of object motion.
Motion graphs, graphical representations of an object’s displacement, velocity, and acceleration over time, provide a powerful tool for understanding the dynamics of moving objects. By studying motion graphs, students can visualize and analyze the intricate relationships between these fundamental quantities, gaining insights into the behavior of objects in motion.
Motion Graphs: Concepts and Definitions
Motion graphs are graphical representations that depict the motion of an object over time. They provide a visual representation of the object’s displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
Different types of motion graphs include:
- Displacement-time graph
- Velocity-time graph
- Acceleration-time graph
Key terms in motion graphs:
- Displacement: The change in position of an object.
- Velocity: The rate of change of displacement.
- Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity.
Interpreting Motion Graphs
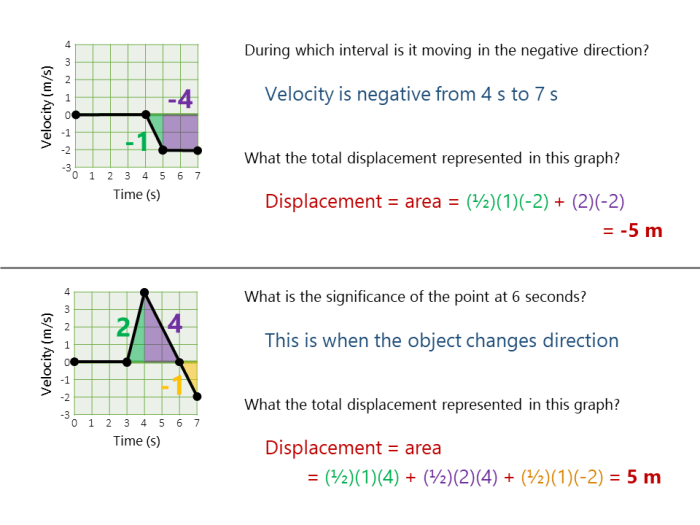
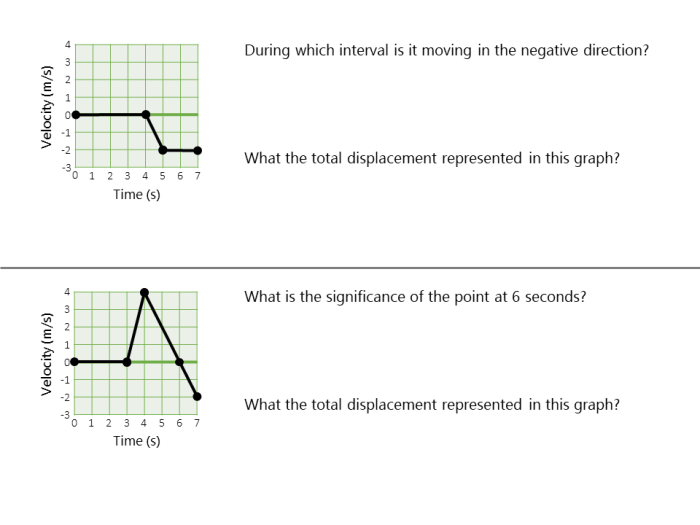
The slope of a motion graph represents the velocity of the object.
To determine the velocity and acceleration of an object from its motion graph:
- Calculate the slope of the graph.
- The slope of the displacement-time graph gives the velocity.
- The slope of the velocity-time graph gives the acceleration.
The shape of a motion graph provides information about the motion of an object:
- A straight line indicates constant motion.
- A curved line indicates changing motion.
- The direction of the slope indicates the direction of motion.
Solving Motion Graph Problems
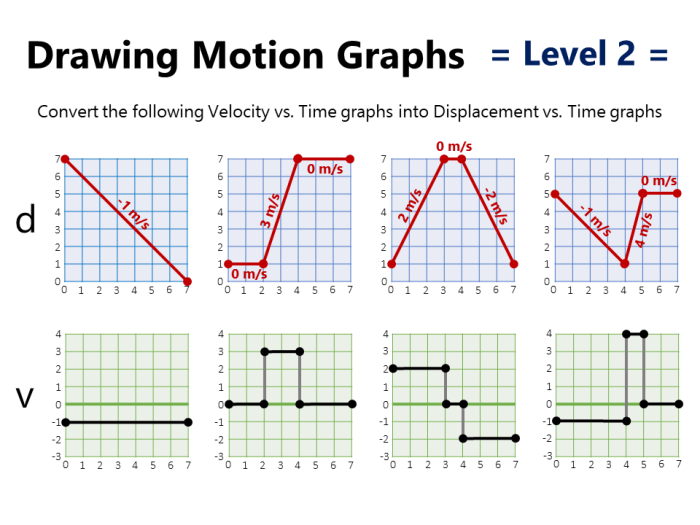
Steps for solving motion graph problems:
- Identify the type of motion graph.
- Determine the slope of the graph.
- Use the slope to calculate the velocity or acceleration.
- Apply relevant equations of motion.
Common problem types and solution strategies:
| Problem Type | Solution Strategy |
|---|---|
| Calculating velocity | Use the slope of the displacement-time graph. |
| Calculating acceleration | Use the slope of the velocity-time graph. |
| Determining motion type | Analyze the shape of the graph. |
Solved examples:
- A car travels 100 m in 10 s. What is its velocity?
- A ball is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 10 m/s. What is its acceleration due to gravity?
Applications of Motion Graphs
Motion graphs have applications in various fields, including:
- Physics
- Engineering
- Sports science
Motion graphs can be used to:
- Analyze the motion of objects
- Predict the motion of objects
- Design experiments
- Solve real-world problems
Examples of motion graph applications:
- Studying the motion of planets
- Designing roller coasters
- Analyzing the performance of athletes
FAQ Summary: Motion Graph Practice Questions Answer Key
What is the significance of motion graphs in physics?
Motion graphs are essential in physics as they provide a visual representation of an object’s motion, allowing physicists to analyze displacement, velocity, and acceleration over time. They facilitate the study of kinematics, the branch of physics concerned with the motion of objects.
How can I effectively utilize the Motion Graph Practice Questions Answer Key?
To maximize the benefits of the Motion Graph Practice Questions Answer Key, approach each question with a problem-solving mindset. Analyze the graph carefully, identify the relevant concepts, and apply the appropriate formulas. Thoroughly review the answer explanations to reinforce your understanding and identify areas for improvement.
What are some common challenges students face when interpreting motion graphs?
Common challenges include determining the slope of the graph to calculate velocity or acceleration, understanding the relationship between the shape of the graph and the object’s motion, and accurately interpreting the graph when the object changes direction or speed.
